DbSchema PostgreSQL ER Diagram Designer
DbSchema is a PostgreSQL ER diagram database designer and query tool. Using DbSchema, you can design and document PostgreSQL databases while connected to the database server or without a connection.
Next, you can share the design with the team using Git. The design model loaded in DbSchema can be compared with the database, synchronization scripts can be generated, and the schema can be deployed to any database server.

How to Connect to PostgreSQL Database
Watch the step-by-step video tutorial below:
For written documentation, please continue reading...
Open DbSchema, then click "Connect to Database" on the Main Screen and choose your database system.
DbSchema will automatically download the required JDBC driver.
Preparing for Connection in DbSchema
Before starting the connection process in DbSchema, ensure the following conditions are met:
- The PostgreSQL Server is running: Verify that the database server is operational and ready to accept incoming connections.
- Firewall Rules : Ensure that the firewall on the server permits traffic through port 5432, which is commonly used for database connections.
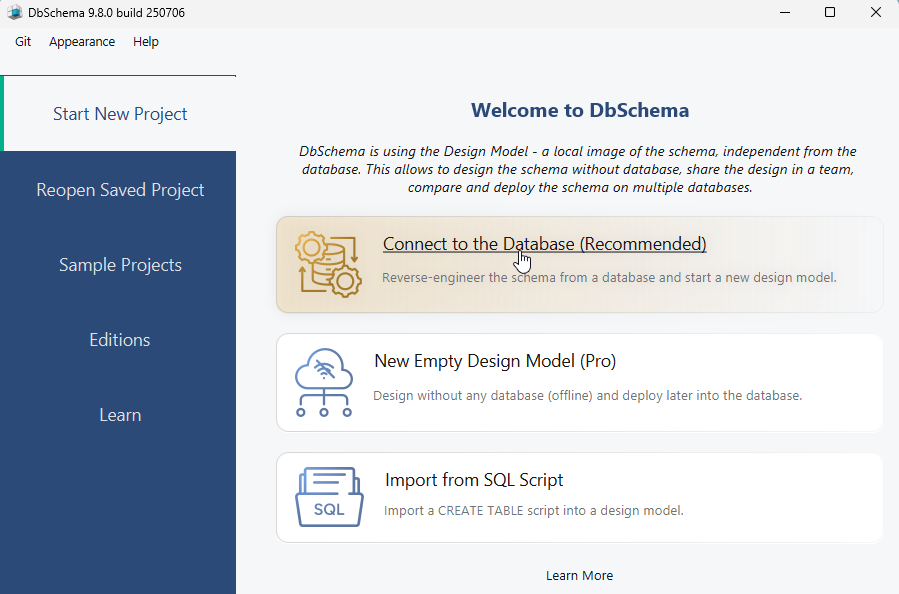
I. Configure the Local Connection in DbSchema
- Select 'Standard' from the JDBC URL
- Connecting to PostgreSQL requires entering the localhost port, along with the database username and password you configured during the PostgreSQL server installation.
- Select the database you want to access, then click 'Connect'.
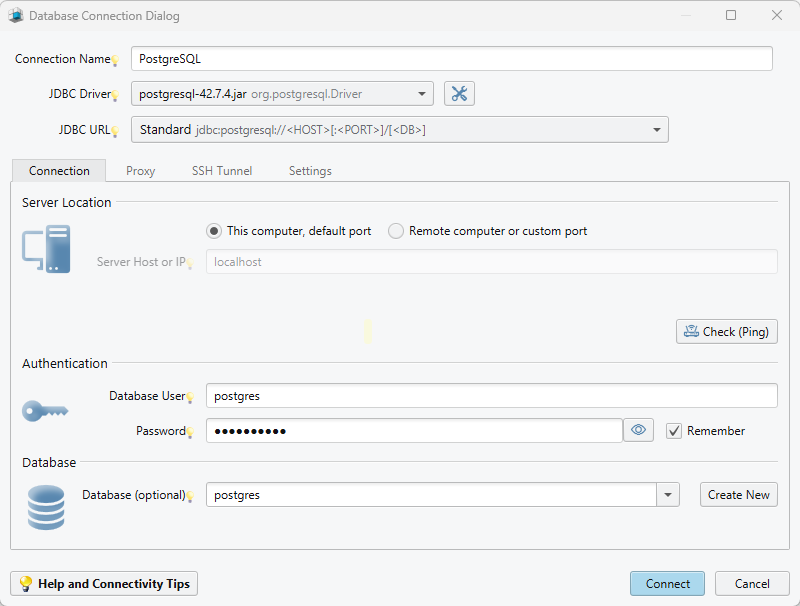
II. Configure the Cloud Connection in DbSchema
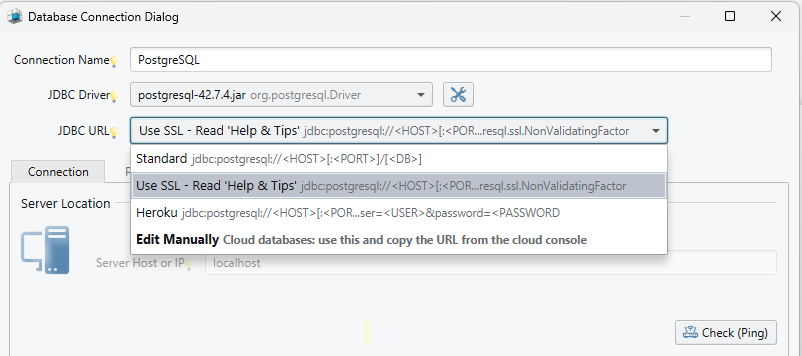
- Select 'Edit Manually' from the JDBC URL
- In DbSchema, you can manually edit the JDBC connection for PostgreSQL, which is particularly useful for connecting to cloud databases.
- You can copy the connection URL from your cloud console and, if needed, adjust it to match your specific setup before testing the connection.
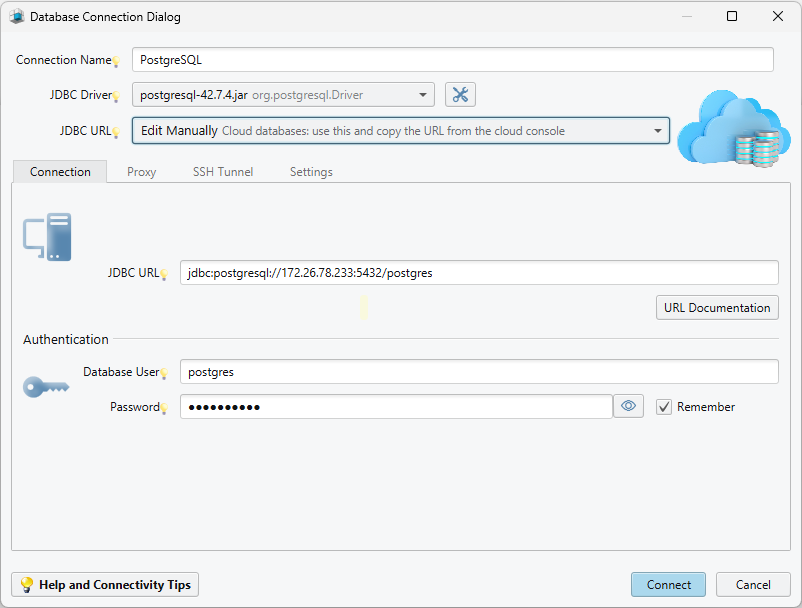
III. Configure the Remote Connection in DbSchema
For remote connections, everything starts with providing the correct combination of username and password.
- To allow remote connections, you need to enable TCP/IP connections in the PostgreSQL configuration.
- Select the Remote computer or custom port
- Here, you can enter the IP address or the Hostname (Windows Computer Name) of your remote PostgreSQL Server to connect from your local computer to another remote machine.
- Test the connection (Ping)
- Now, you have insert the database username and password, allowed to connect from any host.
- Select the database you want to access, then click 'Connect'.
If you fail connecting you may need to check one of the items below.
- Enable Remote Connections
- Change User Password
- Start Postgres Service
- Read the Connection Dialog for more details.
- SSL Connections
- Guided Postgres Installation
- Create Docker Image with System-Stats
Enable Remote Connections
Enable Remote Connections in PostgreSQL
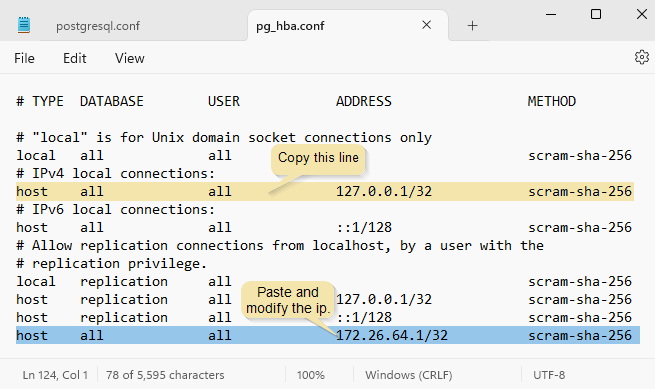
Step 1: Edit pg_hba.conf
On the PostgreSQL server, there is a configuration file called pg_hba.conf. This file controls client authentication.
- On Windows, it is located in the installation folder, usually under
/data. - On Linux, it is typically located in
/var/lib/pgsql/data/or/etc/postgresql/./main/
Edit the pg_hba.conf file and append the following configuration line:
host all all 172.26.64.1/32 scram-sha-256
This allows remote connections from the IP address 172.26.64.1 using the scram-sha-256 authentication method.
Step 2: Restart PostgreSQL
After modifying the pg_hba.conf file, restart PostgreSQL if it's needed to apply the changes:
- On Windows, use the following command:
- On Linux, use the following command:
pg_ctl.exe -D "C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\\data" restart
sudo systemctl restart postgresql
Ensure that PostgreSQL is restarted for the changes to take effect.
Important Security Note
Allowing connections from all hosts (with 0.0.0.0/0) can expose your server to security risks.
It is recommended to specify only the IP addresses or subnets that need access.
Change User Password
You may change a user password from psql using the statement below. The default password is the one you set during Postgres installation.ALTER USER <someUser> PASSWORD '<newPassword>';
Start Postgres Service
If Postgres service is not running, you won't be able to connect.Windows
To enable Postgres Service follow this steps:
- Go to Start -> Control Panel -> System and Security -> Administrative Tools -> Component Services
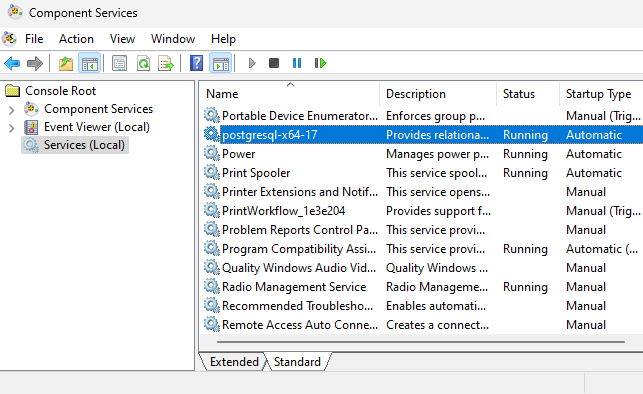
- Open Service Local
- Find your postgres service name setup during installation (For Example: postgresql-9.3)
- Right click on the service name and click start.
Linux
To start the postgres service on linux just type in the console: service postgres start
Allow Postgres Connect Through Firewall
Firewall Rules : Ensure that the firewall on the server permits traffic through port 5432, which is commonly used for database connections.SSL Connections
The certificate you download from AWS is usually in PEM format. You can convert it using:
openssl x509 -outform der -in <mypemcertificate>.pem -out <newdercert>.der
keytool -import -alias <anyname> -keystore <newcertfilename> -file <newdercert>.der
# Keytool may ask for a password to generate the newcert. The new certificate will be available in c:\backup
Edit the DbSchema.vmoptions (located in the same folder as DbSchema.exe or ./DbSchema.app/Contents/vmoptions.txt on Mac OS) and add this parameters:
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=<Full Path of the newcertfilename that you generated>
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=<The password you provided to create the netcertfilename>
-Djavax.net.debug=ssl
In the connection dialog choose 'Use SSL':
How to Install PostgreSQL
Download Postgres- Start the setup...
- Choose the Data Directory:
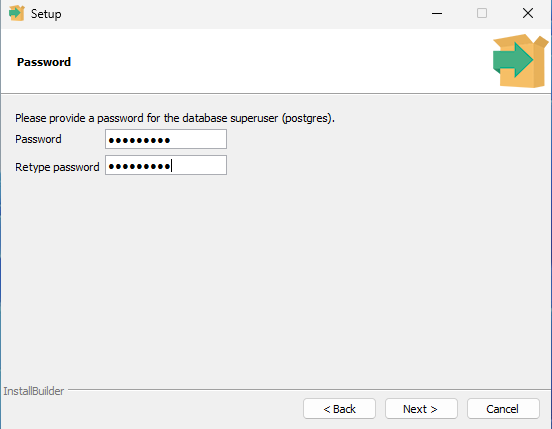
- Choose your password:
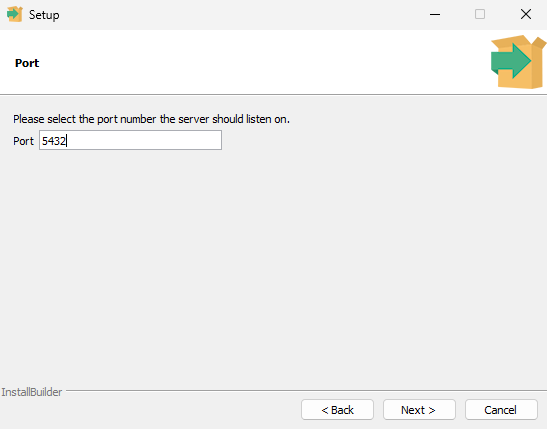
- Select the port number or leave it by default (5432):
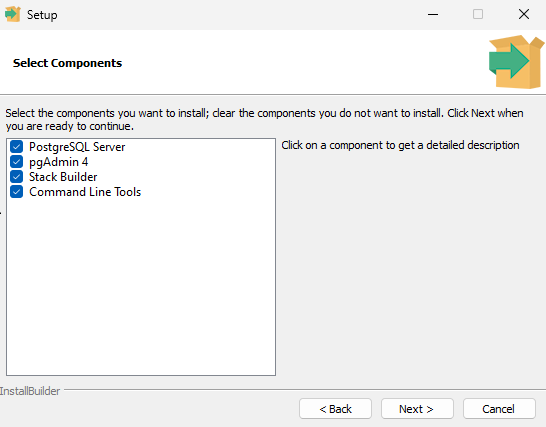
- Select the components you want to install
Create new database
su - postgres// set all to trust
edit /etc/postgres/8.2/main/postgres.sql
pg_ctlcluster 8.2 main restart
or
/etc/init.d/postgres restart
psql -d template1
create database dbtst;
drop database dbtst;
Create a Postgres Docker Container with System-Stats
Use this code to create a docker container with Postgres and System Stats. Save this code snippet to a file Dockerfile without any extension. |
|
|