
What Are Aggregate Functions in SQL? Learn with Examples
Aggregation functions are like mini-calculators inside your database.
Instead of showing each row one by one, they let you perform a calculation across multiple rows, and return just one result.
They’re often used with the GROUP BY clause, which splits the data into smaller groups (like per customer or per product), so you can get one result per group.
Here are the most common SQL aggregation functions:
| Function | What It Does |
|---|---|
MIN() | Returns the smallest value in the column |
MAX() | Returns the highest value in the column |
COUNT() | Counts how many rows are present (ignores NULL, unless using COUNT(*)) |
SUM() | Adds up all values in a numeric column |
AVG() | Calculates the average of all numeric values |
In the next section, we’ll show you each one with examples - both in plain SQL and visually using DbSchema.
Let’s Start with a Simple Example
Imagine this orders table:
| order_id | customer_id | product_name | total_amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 101 | Juice | 25.00 |
| 2 | 102 | Cereal | 32.50 |
| 3 | 101 | Bread | 45.00 |
| 4 | 103 | Milk | 28.00 |
Each row is one order.
For example, customer 101 placed two orders: one for Juice and one for Bread.
1. How many orders do we have?
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM orders;
Returns:
| count |
|---|
| 4 |
2. What is the total revenue?
SELECT SUM(total_amount) FROM orders;
Returns:
| sum |
|---|
| 130.50 |
3. What is the average order value?
SELECT AVG(total_amount) FROM orders;
Returns:
| avg |
|---|
| 32.625 |
4. What is the lowest order value?
SELECT MIN(total_amount) FROM orders;
Returns:
| min |
|---|
| 25.00 |
5. What is the highest order value?
SELECT MAX(total_amount) FROM orders;
Returns:
| max |
|---|
| 45.00 |
GROUP BY - Summarize by Category
If you want to know how much each customer spent in total, you can use GROUP BY:
SELECT customer_id, SUM(total_amount)
FROM orders
GROUP BY customer_id;
This returns:
| customer_id | sum |
|---|---|
| 101 | 70.00 |
| 102 | 32.50 |
| 103 | 28.00 |
So now you know that:
-
Customer 101 bought Juice and Bread, spending a total of $70.00.
-
Customer 102 bought Cereal, spending $32.50.
-
Customer 103 bought Milk, spending $28.00.
Note: Aggregation functions skip over NULL values when doing their calculations - except for COUNT(), which counts all rows, including those with NULLs.
️ Improved Method: Do All of This Visually in DbSchema
You don’t even have to write SQL by hand. Instead, you can use a visual database tool like DbSchema.
In the Query Builder, you can create aggregation queries using just a few clicks - no SQL coding required.
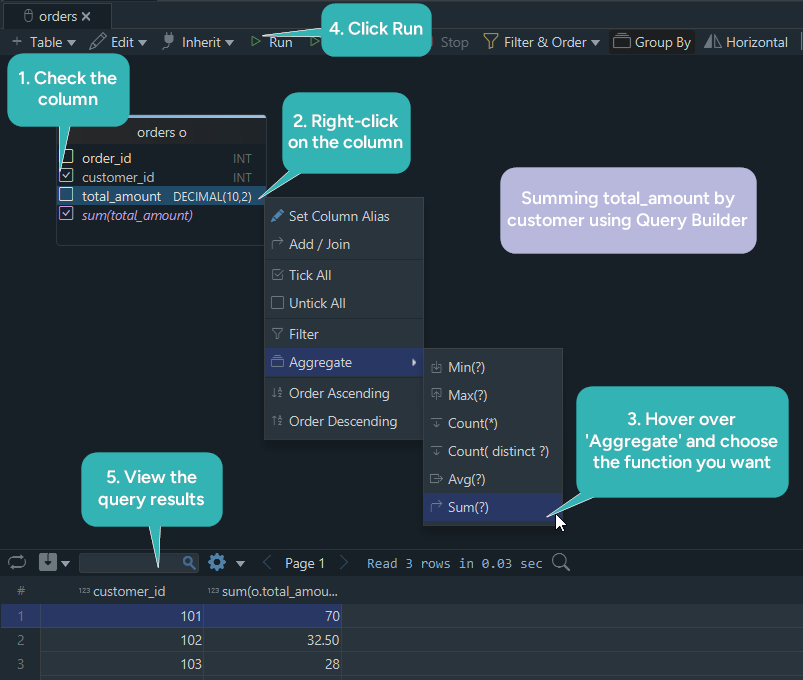
This screenshot shows how to calculate the total amount spent by each customer, step by step, using DbSchema’s visual Query Builder - no SQL needed.
How to Use the Query Builder
-
Open the Query Builder Launch DbSchema and go to the Query Builder tab.
-
Add the Table Drag your
orderstable into the builder area. -
Pick the Columns
- Check the box for
customer_id
- Check the box for
-
Apply an Aggregation
- Right-click on
total_amount - Hover over Aggregate
- Choose
SUM(),AVG(),MIN(), or any other function you need
- Right-click on
-
Group the Results DbSchema will automatically group by any columns that are not aggregated - in this case,
customer_id. -
Run the Query Click Run to see the results instantly.
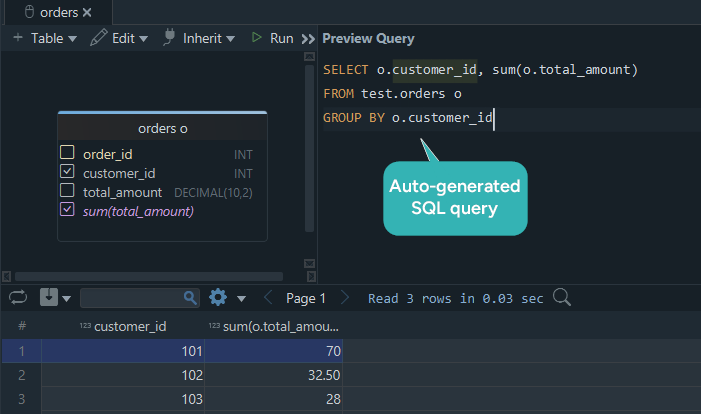
Tip: DbSchema also shows you the SQL it generates, so you can learn while building your queries visually.
Why Aggregation Functions Matter
Aggregation helps you see the big picture in your data:
- Total sales
- Average ratings
- Most frequent values
- Summaries per group (customers, regions, products)
Whether you're analyzing data for school, work, or just exploring - these functions help you understand what’s really happening inside your database.
Final Thoughts
Aggregation functions are some of the most useful, and beginner-friendly features in SQL. And when you use a visual builder like DbSchema, you don’t need to memorize syntax or write code.
Learn More
Download DbSchema Free Visual Query Builder Guide Full SQL Tutorial for Beginners




