How to Create Custom Data Types in DbSchema
Custom data types in DbSchema’s Logical Design help architects enforce consistent column definitions across large models (e.g., all usernames use the same length everywhere).
Important: these types are design-time abstractions. When you deploy to a real database (e.g., MySQL), DbSchema generates the native DBMS type (such as VARCHAR(150)), not the custom name (UserName).
Open Data Type Settings
- Open your project in DbSchema.
- Go to Model → Settings → DBMS Specific → Data Types.
- In the DBMS selector, choose Logical Design.
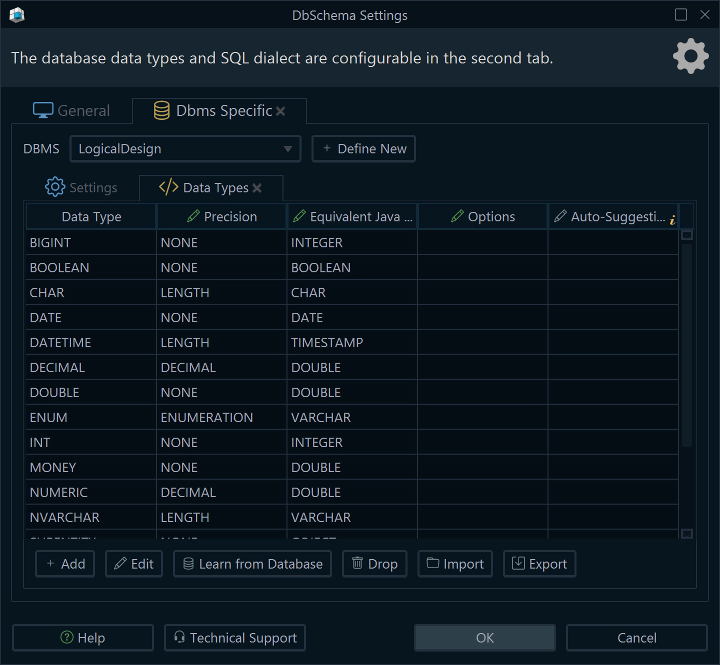
Select Scope
Choose Logical Design to define model-level types.Add New
Create a reusable custom data type.Define a Custom Data Type
- Click + Add New.
- Give the type a clear, descriptive name and set its length:
Examples:
MoneyAmount→DOUBLE, then mapped in Conversion Dictionary to DECIMAL(19,4).CustomerCode→CHAR(10)CreatedAt→TIMESTAMP
- Click OK to save.
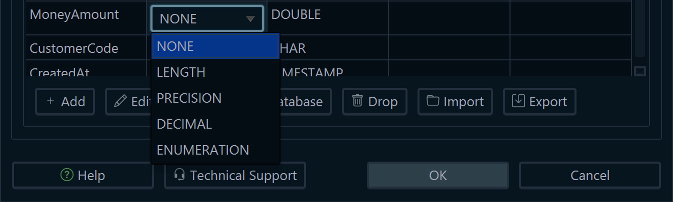
Map the Type for Deployment
Your Logical Design type needs a mapping so that, on deployment, DbSchema generates the correct native DBMS type and precision.
- Open Model → Conversion Dictionary.
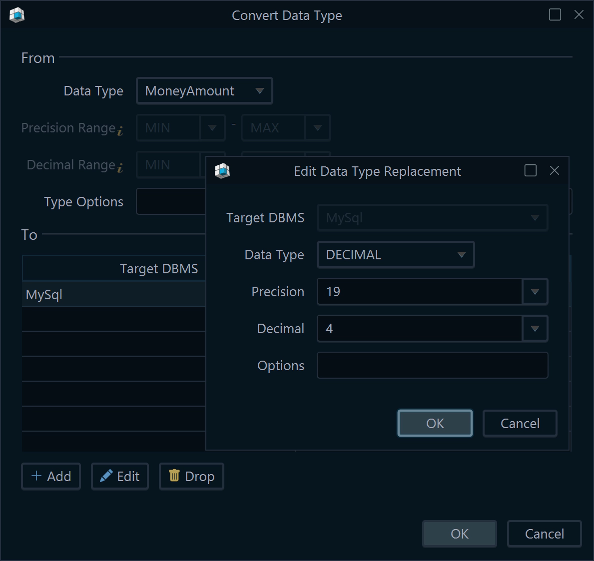
- Click +Data Type, and choose the data type created earlier. (MoneyAmount)
- Choose the target DBMS (e.g., MySQL).
- Map it to the native type and set the exact precision (e.g.,
DECIMAL(19,4)). - Save.
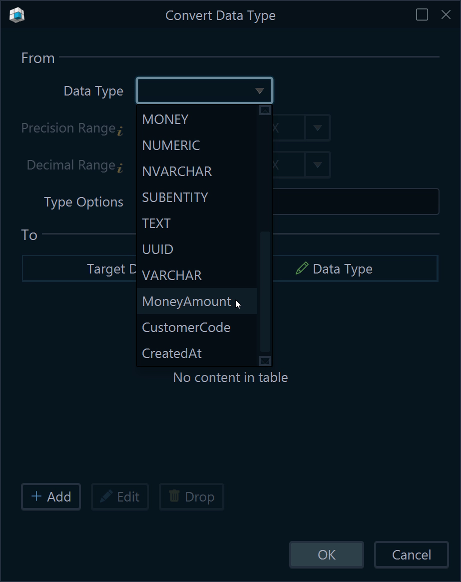
Use the Custom Type in Your Model
- In the column editor, select your custom type (e.g.,
MoneyAmount). - When you generate SQL or deploy, DbSchema applies the mapping and emits the native DBMS type.
Example:
The Logical Design types are now mapped so deployment emits native DBMS types.
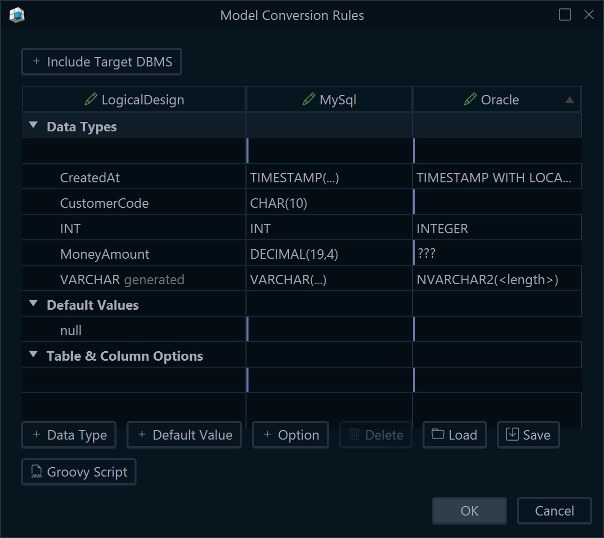
What Happens at Deployment?
- In the model: you work with logical names like
MoneyAmount,CustomerCode,CreatedAt. - On deployment: DbSchema automatically converts each logical type to the mapped native DBMS type (e.g.,
MoneyAmount → DECIMAL(19,4),CustomerCode → CHAR(10),CreatedAt → TIMESTAMPin MySQL). - No extra steps: the SQL generator uses your Conversion Dictionary; you can preview the exact DDL in Schema Compare / Generate SQL before applying.
- In the database: developers will see only the native types (e.g.,
DECIMAL(19,4),CHAR(10),TIMESTAMP) produced by these mappings.
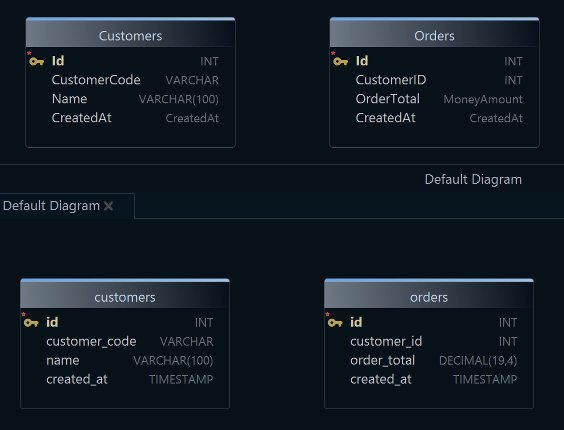
Logical Design
Physical Design
Troubleshooting
- “Length required” prompts in MySQL UI: expected only if you use a DBMS-specific type. For Logical Design types, set the length in the type definition and the exact DBMS length in the Conversion Dictionary.
- Custom name not visible in DB: by design. Logical Design names are model-level abstractions. The DB stores native types.
Summary
- Create custom types in Logical Design to standardize columns.
- Use the Conversion Dictionary to map each type to the exact native DBMS type (MoneyAmount → to DECIMAL(19,4) in MySQL).
- On deployment, DbSchema converts Logical Design names to native types, ensuring consistency without leaking modeling abstractions into the database.
Next Step
Want to try this out yourself? Download DbSchema Free Trial and start designing with custom data types today.
You may also find these guides helpful: