
DbSchema | How to Create Indexes in SQLite?

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Prerequisites
- What is an Index?
- The Usage of Indexes
- Advantages and Limitations of Using an Index
- Types of Index
- Creating an Index in sqlite3
- Creating an Index in DbSchema
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
In any relational database, managing and organizing data effectively is key to maintaining good performance. Indexes play an integral role in this aspect by improving data retrieval speed. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of how to create indexes in SQLite using sqlite3 and DbSchema.
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of SQL and relational databases
- SQLite3 installed on your local system
- DbSchema installed on your local system
For installation and establishing connection you can read our article SQLite-How to create a database?
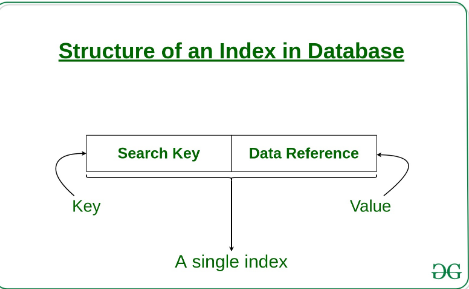
What is an Index?
An index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table. It works similarly to an index in a book, providing a quick way to access the content without going through each page. The index in databases does this by creating a data structure that can be quickly traversed to find the location of a data record.
The Usage of Indexes
Indexes are mainly used to speed up the retrieval of data from the database. They are exceptionally efficient in situations where there is a large amount of data, and you need to perform queries to retrieve data based on some conditions.
Advantages and Limitations of Using an Index
Advantages:
- Improved Query Speed: Indexes significantly enhance the speed of data retrieval operations in a database.
- Efficient Data Sorting: They aid in returning sorted data faster.
- Rapid Record Management: Indexes enhance the speed of operations such as insert, update, and delete with WHERE clauses.
Limitations:
- Space Requirement: Indexes require additional space on the disk.
- Impact on Insertion, Deletion, and Update Operations: Since indexes require continuous maintenance, insert, update, and delete operations become slower.
Types of Index
| Index Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Unique Index | This type of index ensures that all the values in the index are unique. |
| Composite Index | This is an index on two or more columns of a table. |
| Implicit Index | SQLite automatically creates an implicit index when we create a UNIQUE constraint or a PRIMARY KEY constraint. |
Creating an Index in sqlite3
Step 1: Open SQLite3
Start by opening your SQLite3 console. You can do this by typing sqlite3 in your terminal or command prompt.
|
Step 2: Connect to Your Database
Connect to your database using the .open command followed by the database name. If the database doesn’t exist, SQLite3 will create it. Here is an example:
|
To know more about creating a database you can read our article SQLite-How to create a database?
Step 3: Create or Connect to Your Table
If you’re starting a new database, you’ll need to create a table. If you’re connecting to an existing database, you can skip this step.
Here is an example of how to create a table:
|
To know more about creating a table you can read our article SQLite-How to create a Table?
Step 4: Create a Non-Unique Index:
Now you can create a non-unique index using the CREATE INDEX SQL command. This will create an index on the name column:
|
Here, __idx_student_name` is the index name.
Step 5: Create a Unique Index:
If you wish to create a unique index that ensures all values in the index are unique, use the CREATE UNIQUE INDEX command:
|
Here, __idx_student_id` is the unique index name.
Step 6: Check Index:
Finally, you can check whether your index has been created correctly using the .indices command followed by the table name:
|
Creating an Index in DbSchema
Step 1: Launch DbSchema
Start the DbSchema software. You will be greeted with the Connect to Database window.
Step 2:Create a New Connection
Click on the Create New Connection button. A new window will pop up.
Step 3:Set Connection Details
In this new window, choose the DBMS as SQLite, provide the necessary information such as the database file (or choose to create a new one), and click on the Test Connection button to ensure the settings are correct. Once verified, click on the Connect button.
Step 4:Select Table
In the main DbSchema window, you will see your database’s schema. Right-click on the table where you want to create an index, and select Open in Diagram. This will open a new window with the table schema.
Step 5:Navigate to the Indexes Tab
In this window, you’ll see a tab named Indexes / Foreign Keys. Click on this tab to see the current indexes and create new ones.
Step 6:Create a New Index
Click on the New Index button, and a new window will pop up. In this window, provide the index name, select the index type (Unique or Not Unique), and add the required columns to the index.
Step 7:Save the Index
Once you have provided the necessary information, click on the Save button. This will create the index, and you will see it in the Indexes / Foreign Keys tab.
Step 8:Apply Changes
To make sure the changes are applied to the actual database, go to the main DbSchema window and click on the Refresh button.
Visually Manage SQLite using DbSchema
DbSchema is a SQLite client and visual designer. DbSchema has a free Community Edition, which can be downloaded here.
Key Features of DbSchema:
Following are the key features of DbSchema which distinguish it from other database GUI tools.
Conclusion
Indexes play an integral role in enhancing the speed of data retrieval in databases. This article provided an in-depth understanding of what indexes are, their types, and how to create them in SQLite using sqlite3 and DbSchema. Despite the benefits, remember that indexes come with their limitations. Careful thought should be put into when and where to use them.




